In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a transformative force, reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. As the capabilities of AI continue to expand, it is essential to understand the nuances and implications of this revolutionary field.
The Fundamentals of AI

Understanding the Basics of AI
AI is a broad term that encompasses the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. These systems are designed to mimic the cognitive abilities of the human mind, often surpassing them in certain domains.
| Key Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | A subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable systems to perform specific tasks effectively without explicit programming. |
| Deep Learning | A more advanced form of machine learning that utilizes artificial neural networks, inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, to process and analyze complex data. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | A field of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human language, enabling systems to understand, interpret, and generate human-like text. |
- The fundamentals of AI include the development of algorithms, the use of large datasets, and the advancement of computational power.
- AI-powered systems are used in a wide range of applications, from personal digital assistants to autonomous vehicles and medical diagnostics.
- The field of AI is constantly evolving, with new breakthroughs and innovations emerging at a rapid pace.
The History and Evolution of AI
The concept of AI has been around for centuries, with early pioneers laying the groundwork for the field. The term “artificial intelligence” was coined in the 1950s, and since then, the field has undergone significant advancements.
- Early Developments (1950s-1970s): During this period, researchers focused on developing rule-based systems and exploring the potential of machines to mimic human cognitive functions.
- The AI Winter (1970s-1980s): This period was characterized by a decline in funding and enthusiasm for AI, as the field faced challenges in achieving the expected breakthroughs.
- The Resurgence of AI (1980s-2000s): The rise of powerful computers, the availability of large datasets, and advancements in machine learning algorithms led to a renewed interest in AI.
- The Current Era (2000s-present): The rapid growth of computational power, the abundance of data, and the development of deep learning techniques have fueled the recent surge in AI capabilities and applications.
Today, AI is being applied in a wide range of industries, from healthcare and finance to transportation and education, transforming the way we live and work.
The Impact of AI on Society
The integration of AI into various aspects of our lives has had a significant impact on society, both positive and negative.
- Automation and Employment: AI-powered automation has the potential to disrupt traditional job markets, leading to concerns about job displacement and the need for workforce retraining.
- Ethical Considerations: As AI systems become more sophisticated, there are growing concerns about issues such as bias, transparency, and the accountability of AI-powered decision-making.
- Privacy and Data Security: The increasing reliance on data and the deployment of AI-powered systems raise important questions about data privacy, consent, and the protection of personal information.
- Emerging Challenges: The rapid pace of AI development has led to new challenges, such as the potential for AI-powered misinformation, the risks of AI-enabled cyberattacks, and the ethical dilemmas surrounding the use of AI in sensitive domains like healthcare and law enforcement.
Understanding and addressing these societal implications of AI is crucial as we continue to navigate the complex landscape of this transformative technology.
The Applications of AI
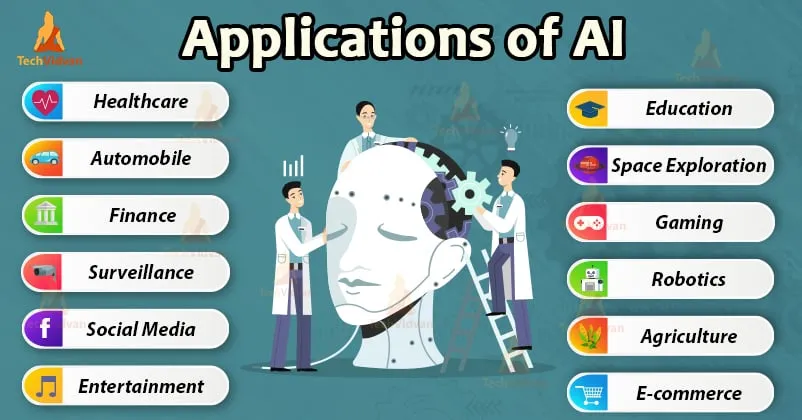
AI in Healthcare
The integration of AI in the healthcare industry has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach medical diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
- Predictive Analytics and Early Disease Detection: AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns and predict the onset of diseases, enabling early intervention and improved patient outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: AI algorithms can help tailor treatments and therapies to individual patients, based on their unique genetic profiles and medical history.
- Automated Diagnosis and Decision Support: AI-powered systems can assist healthcare professionals in making more accurate and efficient diagnoses, as well as providing data-driven recommendations for treatment plans.
- Enhancing Workflow Efficiency: AI-powered automation can streamline various administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments, processing insurance claims, and managing electronic health records.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Improved accuracy in disease detection and diagnosis – Personalized and targeted treatments – Increased efficiency in healthcare delivery | – Ensuring data privacy and security – Addressing bias and fairness in AI-powered systems – Gaining trust and acceptance from healthcare professionals and patients |
- AI-powered technologies are being adopted in various healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
- The integration of AI in healthcare has the potential to enhance patient outcomes, improve resource allocation, and reduce overall healthcare costs.
AI in Finance and Banking
The finance and banking sectors have been at the forefront of AI adoption, leveraging the technology to improve decision-making, enhance customer experience, and reduce risks.
- Fraud Detection and Anti-Money Laundering: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify suspicious patterns and detect fraudulent activities in real-time.
- Personalized Financial Advice and Wealth Management: AI-powered robo-advisors can provide tailored investment recommendations and portfolio management services based on individual risk profiles and financial goals.
- Credit Risk Assessment: AI models can analyze a wide range of data points to assess the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses, enabling more accurate and efficient credit decisions.
- Automated Trading and Investment Strategies: AI-powered trading systems can analyze market data, identify patterns, and execute trades at speeds and scales beyond human capabilities, potentially improving investment returns.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Enhanced fraud detection and risk management – Personalized financial services and customer engagement – Improved investment strategies and portfolio optimization | – Ensuring transparency and explainability of AI-powered decisions – Addressing ethical concerns around the use of AI in high-stakes financial decisions – Maintaining compliance with regulatory standards |
- The financial services industry has been an early adopter of AI, with applications ranging from customer service and lending to investment management and regulatory compliance.
- The integration of AI in finance has the potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall customer experience.
AI in Transportation and Logistics
The transportation and logistics sectors have embraced AI to optimize operations, improve safety, and enhance the customer experience.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Mobility: AI-powered self-driving cars, trucks, and other transportation modes are being developed to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and provide more accessible mobility options.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources to optimize supply chain operations, including inventory management, route planning, and demand forecasting.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems can monitor the condition of transportation assets, such as vehicles and infrastructure, and predict when maintenance is required, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Intelligent Traffic Management: AI-powered systems can analyze real-time traffic data and adjust signal timings, reroute traffic, and provide personalized navigation recommendations to improve overall transportation network performance.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Improved safety and reduced accidents through autonomous vehicles – Enhanced efficiency and cost savings in supply chain operations – Optimized transportation network performance and reduced congestion | – Ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles – Addressing regulatory and ethical concerns around the deployment of AI-powered transportation systems – Overcoming infrastructure and technological barriers to widespread adoption |
- The transportation and logistics sectors are at the forefront of AI adoption, with applications that span from self-driving cars and smart traffic management to predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization.
- The integration of AI in transportation and logistics has the potential to improve safety, increase efficiency, and provide a better user experience for both businesses and consumers.
AI in Retail and E-commerce
The retail and e-commerce industries have been leveraging AI to enhance customer engagement, optimize operations, and drive sales.
- Personalized Recommendations and Product Suggestions: AI-powered recommender systems can analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns to provide personalized product recommendations and tailored shopping experiences.
- Automated Inventory Management and Demand Forecasting: AI algorithms can analyze sales data, market trends, and other relevant information to optimize inventory levels, streamline logistics, and accurately forecast future demand.
- Conversational AI and Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can engage in natural language interactions with customers, providing real-time support, answering questions, and assisting with various tasks.
- Computer Vision and Augmented Reality: AI-powered computer vision and augmented reality technologies can enhance the online shopping experience by allowing customers to virtually try on products or visualize them in their own environments.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Improved customer engagement and personalized shopping experiences – Optimized inventory management and demand forecasting – Streamlined customer service and enhanced operational efficiency | – Ensuring the ethical and responsible use of customer data – Addressing bias and fairness in AI-powered recommendation systems – Integrating AI seamlessly with existing retail and e-commerce infrastructures |
- The retail and e-commerce industries have been quick to adopt AI-powered technologies, leveraging them to enhance the customer experience, improve operational efficiency, and drive sales.
- The integration of AI in retail and e-commerce has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses interact with and serve their customers.
AI in Education
The education sector has started to embrace the potential of AI to personalize learning, enhance teaching methods, and improve student outcomes.
- Adaptive Learning and Personalized Instruction: AI-powered adaptive learning platforms can analyze student performance, learning styles, and progress to tailor educational content and delivery to individual needs.
- Automated Grading and Feedback: AI algorithms can assist educators in the grading process, providing immediate feedback and insights to students, while freeing up teachers’ time for more meaningful interactions.
- Intelligent Tutoring Systems: AI-powered virtual tutors can provide personalized guidance, answer questions, and offer learning support to students, complementing the role of human teachers.
- Educational Analytics and Insights: AI-powered analytics can help educators and administrators gain deeper insights into student performance, attendance patterns, and other key metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making and resource allocation.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Personalized and adaptive learning experiences – Improved feedback and assessment mechanisms – Enhanced teacher-student interactions and resource allocation | – Ensuring equitable access to AI-powered educational tools – Addressing concerns about the impact of AI on human-centric teaching methods – Maintaining privacy and security of student data |
- The adoption of AI in education is still in the relatively early stages, but the potential benefits are significant, including improved learning outcomes, increased engagement, and more efficient resource utilization.
- Collaboration between education professionals, technology experts, and policymakers is crucial to ensure the ethical and responsible integration of AI in the education sector.
The Future of AI

Emerging Trends and Innovations in AI
As AI continues to evolve, a range of emerging trends and innovations are shaping the future of the technology.
- Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP): Improvements in NLP are enabling more natural and contextual language interactions between humans and machines, paving the way for more seamless communication.
- Reinforcement Learning and Generative AI: Advancements in reinforcement learning and the development of generative AI models are enabling the creation of more autonomous and creative AI systems.
- Edge Computing and Embedded AI: The integration of AI capabilities at the edge, closer to the source of data, is enabling real-time decision-making and reducing the reliance on cloud-based infrastructure.
- Ethical and Responsible AI: There is a growing emphasis on developing AI systems that adhere to ethical principles, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Multimodal AI: The convergence of different AI modalities, such as computer vision, speech recognition, and natural language processing, is enabling more comprehensive and holistic AI-powered solutions.
| Emerging Trends | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| – Advancements in NLP – Reinforcement learning and generative AI – Edge computing and embedded AI – Ethical and responsible AI – Multimodal AI | – More natural and intuitive human-machine interactions – Increased autonomy and creativity in AI systems – Real-time decision-making and reduced latency – Enhanced trust and transparency in AI applications – Comprehensive and versatile AI-powered solutions |
- These emerging trends and innovations in AI are shaping the future of the technology, paving the way for more advanced, intelligent, and responsible AI systems.
- The continued evolution of AI will have far-reaching implications across various industries and sectors, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with technology.
Potential Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As AI continues to advance, it is essential to address the potential challenges and ethical considerations associated with its development and deployment.
- Bias and Fairness: Ensuring that AI systems are free from bias and discrimination, and that they make fair and equitable decisions, is a critical concern.
- Accountability and Transparency: Establishing clear lines of accountability and ensuring transparency in the decision-making processes of AI-powered systems is crucial for building trust and acceptance.
- Privacy and Data Security: Protecting the privacy of individuals and ensuring the secure handling of sensitive data is a key consideration as AI systems become increasingly reliant on data.
- Job Displacement and Workforce Retraining: The integration of AI-powered automation has the potential to disrupt traditional job markets, necessitating the need for workforce retraining and the development of new skills.
- Societal and Ethical Implications: The widespread adoption of AI raises broader societal and ethical questions, such as the impact on human autonomy, the potential for AI-powered surveillance, and the need for robust governance frameworks.
| Challenges | Potential Approaches |
|---|---|
| – Bias and fairness – Accountability and transparency – Privacy and data security – Job displacement and workforce retraining – Societal and ethical implications | – Developing AI systems with built-in safeguards against bias and discrimination – Establishing clear guidelines and frameworks for the governance of AI – Implementing robust data privacy and security measures – Investing in workforce retraining and the development of new skills – Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and public dialogue on the ethical implications of AI |
- Addressing these challenges and ethical considerations is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of AI, ensuring that the technology benefits society as a whole.
- Collaboration between policymakers, industry leaders, and experts from diverse fields is essential in shaping the future of AI and ensuring its alignment with societal values and principles.
Conclusion
The rise of Artificial Intelligence has profoundly transformed our world, revolutionizing industries, enhancing human capabilities, and reshaping the way we live and work. From healthcare and finance to transportation and education, AI-powered technologies are driving unprecedented advancements, unlocking new possibilities and opportunities.
As we continue to navigate the rapidly evolving AI landscape, it is essential to recognize the immense potential of this transformative technology, as well as the challenges and ethical considerations that come with its development and deployment. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, promoting responsible innovation, and addressing the societal implications of AI, we can harness the power of this technology to create a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous future for all.
The journey ahead may be filled with both opportunities and complexities, but by embracing the promise of AI and working collectively to address its challenges, we can shape a tomorrow that is more intelligent, efficient, and aligned with our shared values. The future of AI is ours to define, and the choices we make today will have a lasting impact on the world we leave behind.